Asset Management For City Sustainability and Resiliency Goals
By Shannon McGrath, Director of Asset Management and Jack Woolery, Asset Management Specialist, WSB
July 15, 2024
Cities exploring ways to maintain and improve infrastructure sustainably cannot overlook asset management. Thorough data collection and a thoughtful asset management plan can provide the necessary recommendations needed to mitigate weather-based risk, as well as ensure communities are reaching climate goals through green infrastructure strategies.
How can asset management further sustainability and resiliency goals for your community’s infrastructure? Here are some things to consider.
Data and Technology
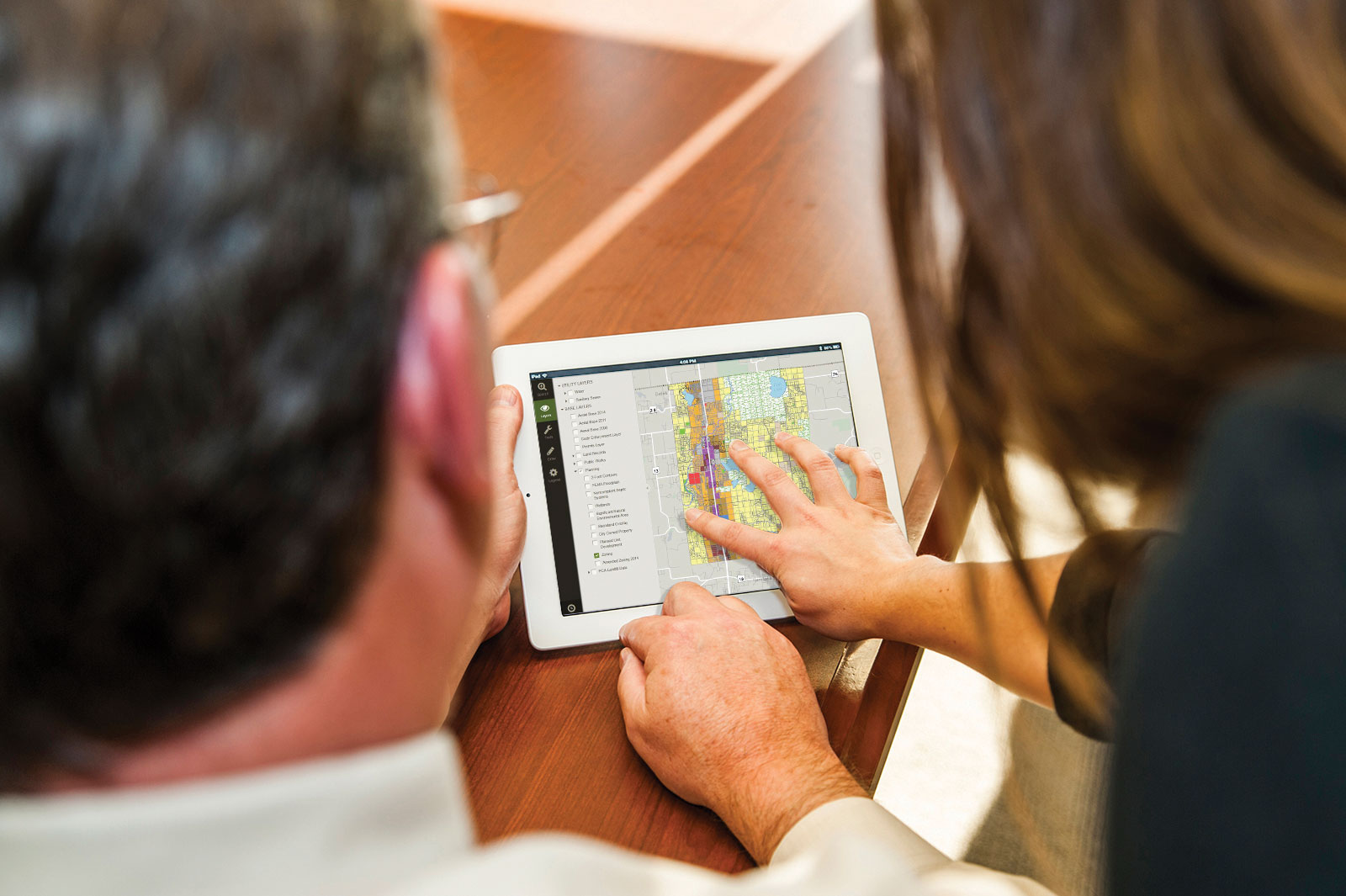
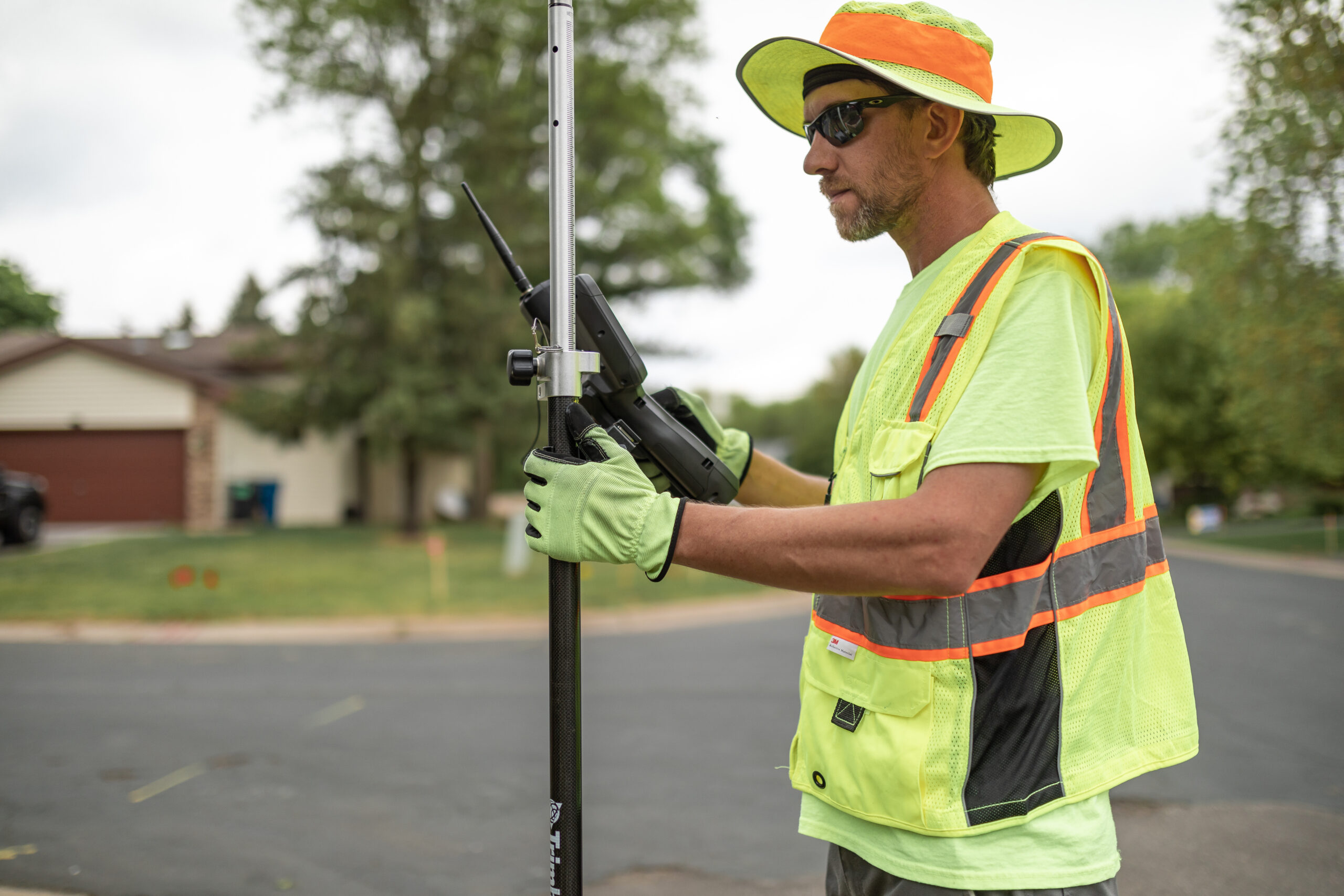
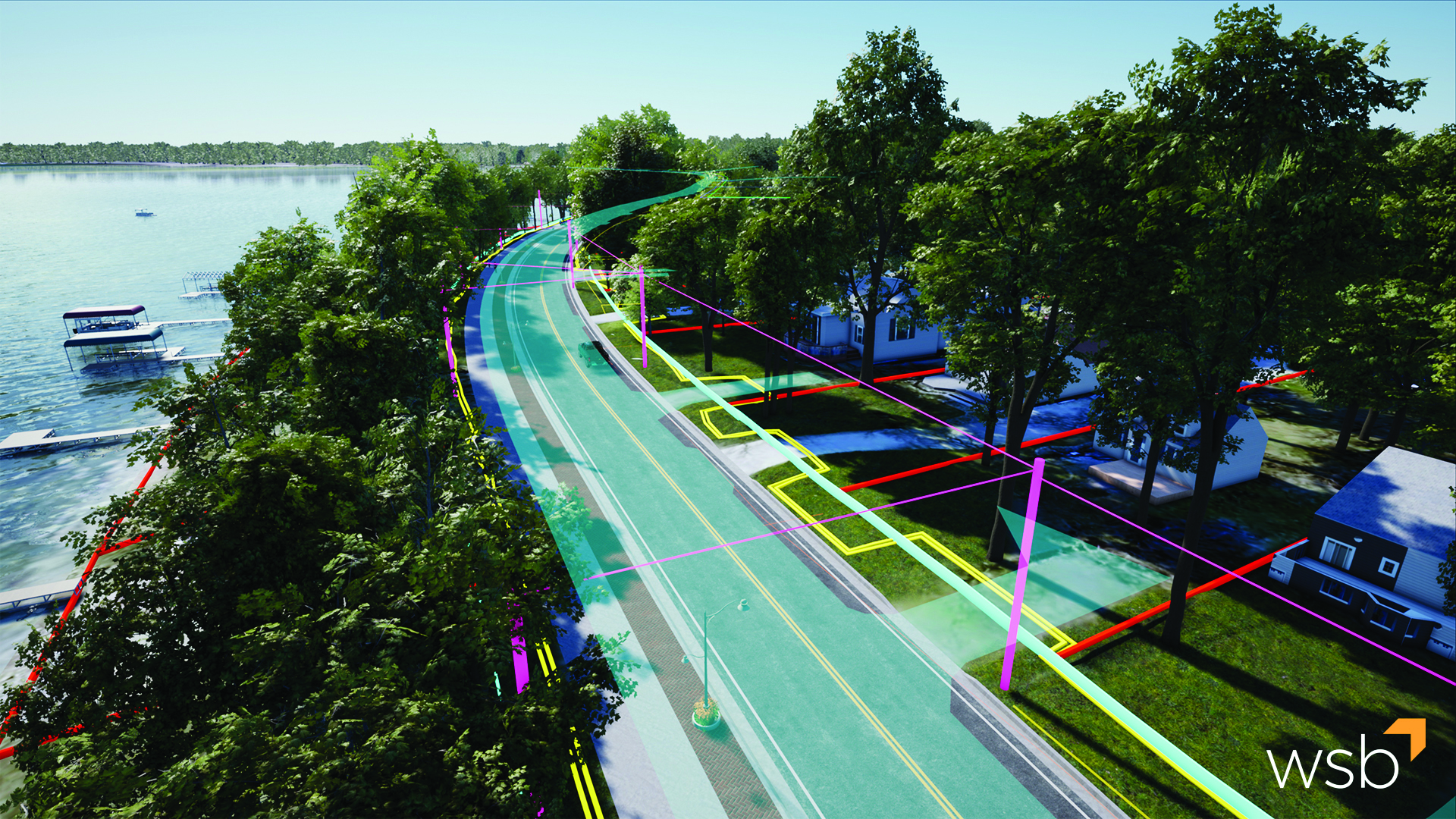
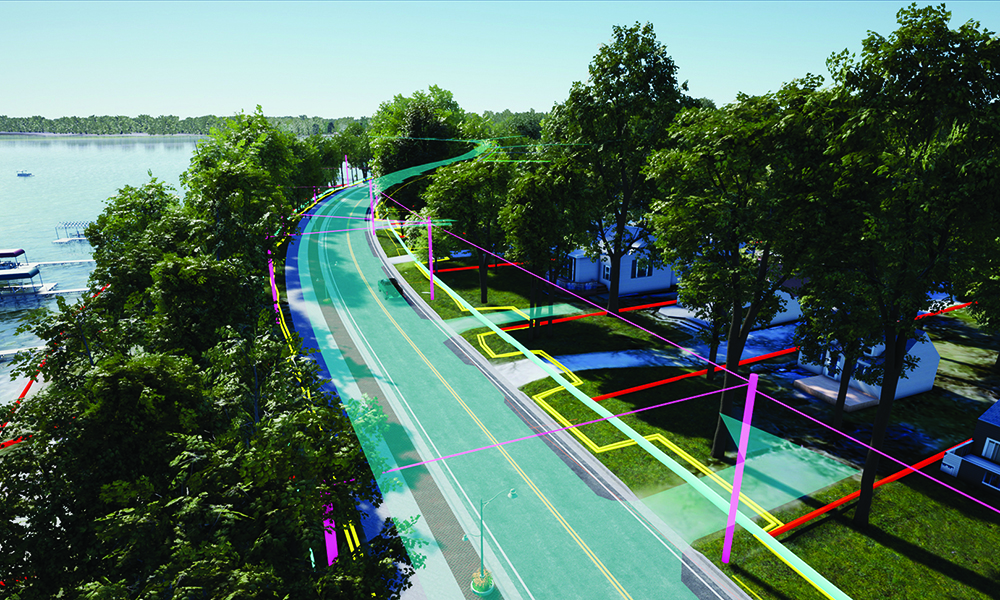
Good data is the key to asset management. Data collection can be done through visual field inspections or using technology such as Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR). In visual inspections, expert(s) travel to each individual asset to collect data and provide more detailed information than could be acquired through inspecting photos and maps.
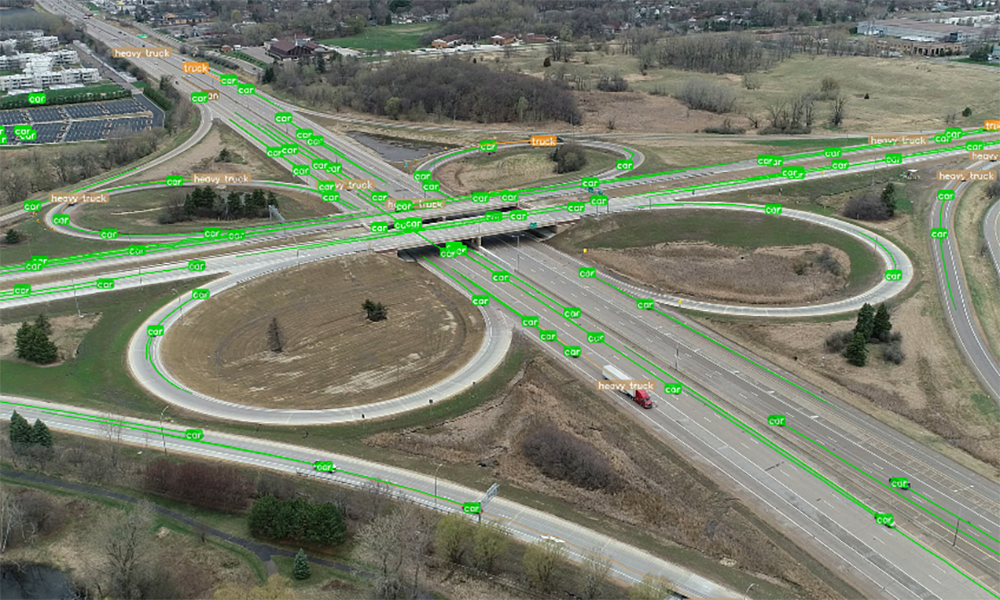
Conversely, LIDAR is a remote sensing technique that uses light to make measurements and collect geographic locations for all above-ground infrastructure. The light pulses create a three-dimensional image that models the infrastructure with useful measurement data.
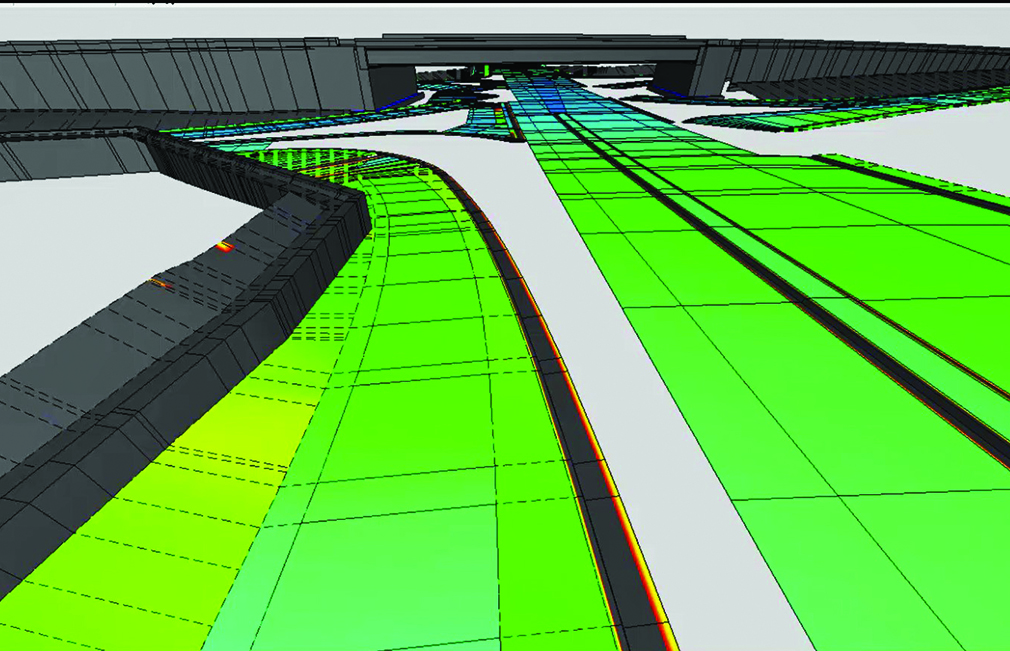
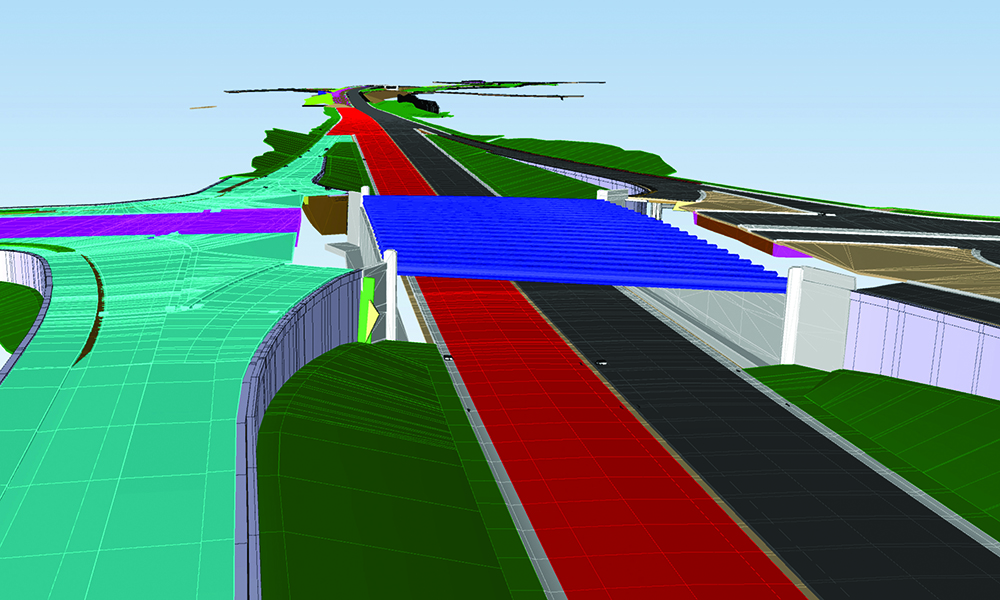
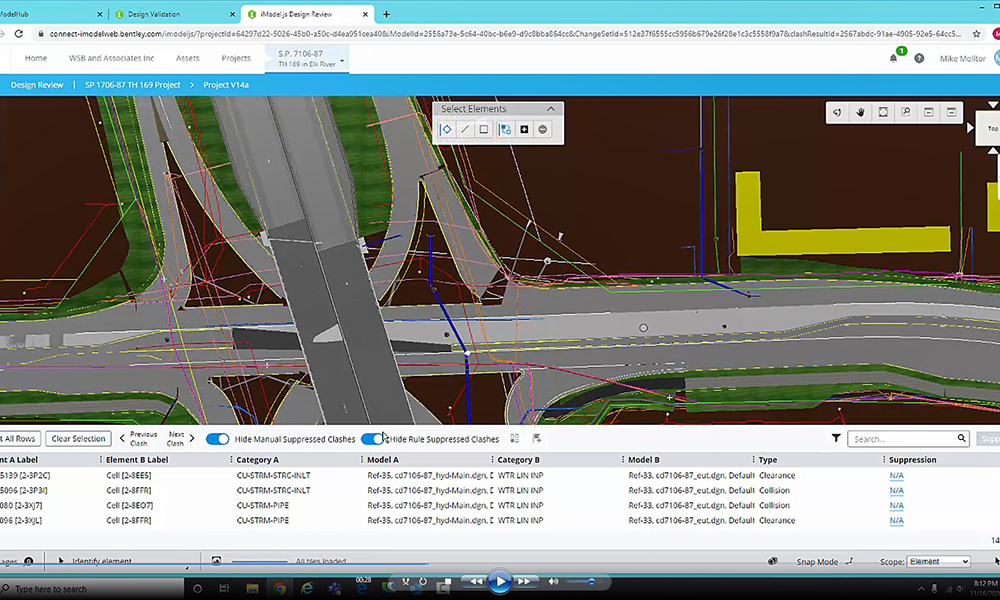
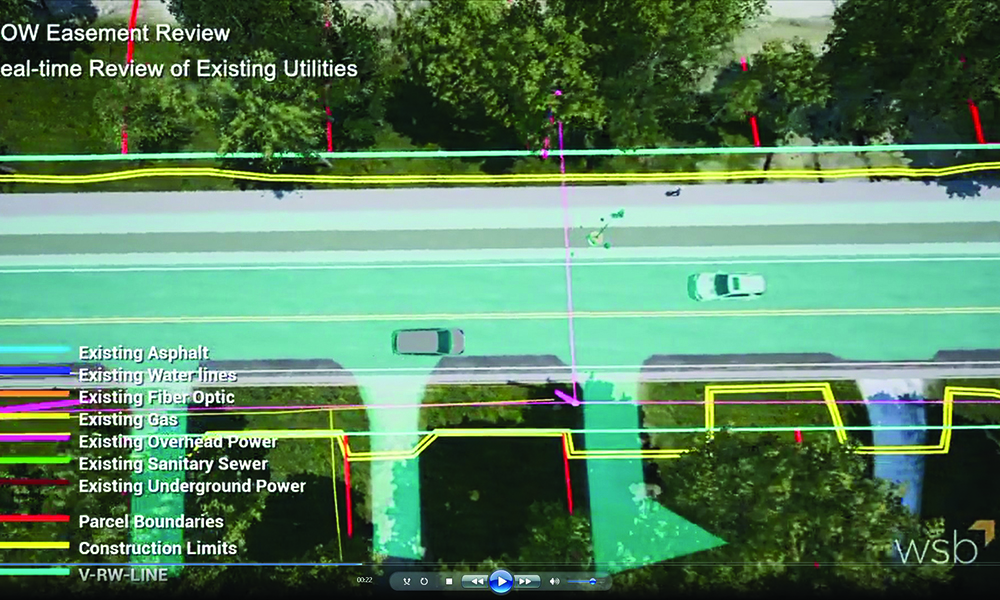
Using an Asset Management System (AMS) integrated with a Geographic Information System (GIS), any data collection can be combined with information like a site’s physical condition, soil quality, traffic volumes and an asset’s vulnerability to extreme weather events like flooding for better risk-based planning and prioritization. Additionally, water and wastewater assets may implement a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system, so system monitoring is further automated which reduces the number of in-person trips required while also providing asset stakeholders or elected officials ease of access to the information they need. To further that point, an AMS paired with 3D modeling provides an easier means of communication between internal stakeholders (e.g. planning, design, construction and asset management) and external stakeholders (e.g. elected officials and the public). The combination of expert analysis and technologies provides the information necessary to optimize an asset’s longevity.
Risk Assessment and Management
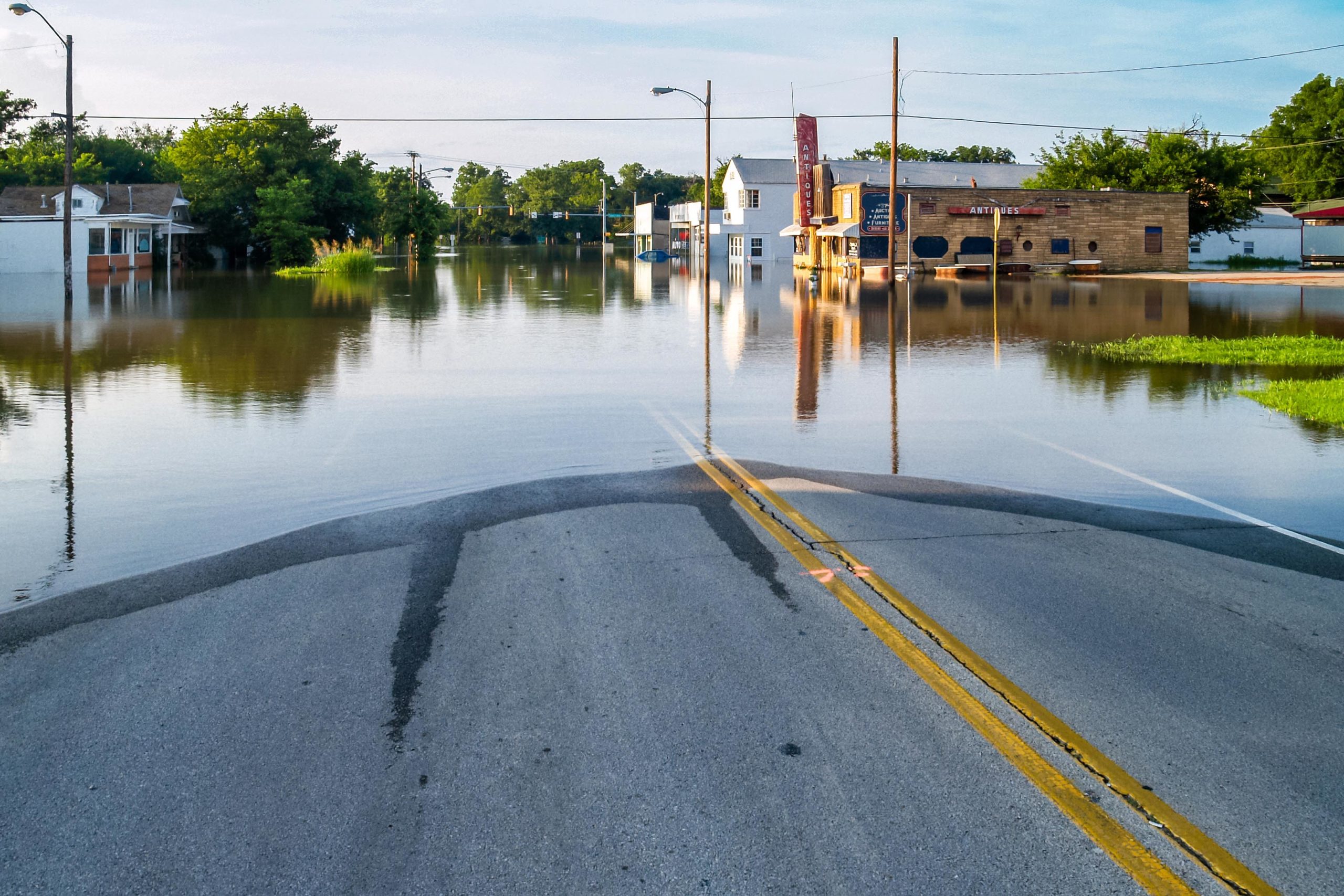
Identifying risk and risk mitigation strategies greatly improves asset resilience against risks such as extreme weather events and premature deterioration. This risk assessment can be broken down in two ways – an enterprise risk assessment and an asset level risk assessment.
With an enterprise risk assessment, locations with heightened risk of extreme weather events are subjected to an enterprise assessment which is larger in scale and can cover a sizable geographic area like a whole community, region or state. For example, communities prone to flooding may have a flood vulnerability model developed as part of an enterprise risk assessment with recommendations for new projects and upgrading current assets.
On a smaller scale, an asset level risk assessment inspects an individual asset rather than a larger location. Through an asset level risk assessment, for example, a roadway is examined to identify underground utilities, asset condition and impact of failure such as impacting a critical healthcare facility or a residence. Factors such as soil type and its impact on pipe corrosion could also be considered.
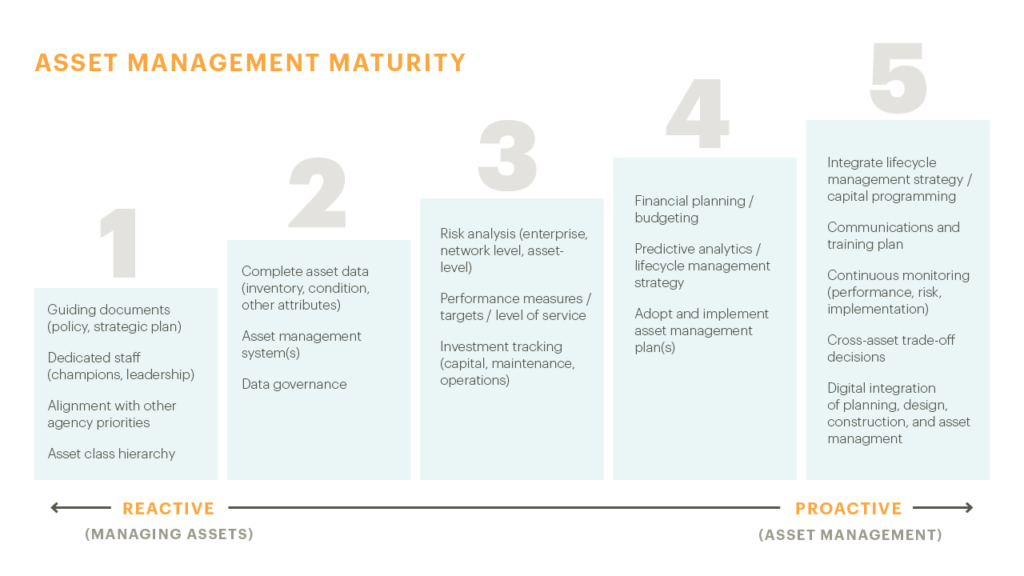
Risk assessment is tailored to fit both qualitative and quantitative approaches like climate modeling for a region or coordinating with long tenured staff and agencies with institutional knowledge on what best practices have worked for a particular asset. Risk assessments and asset management plans provide ways to improve resiliency and sustainability, prioritize mitigation strategies and costs in financial planning and prevent the loss of institutional knowledge, cutting down on unnecessary work repetition.
Incentivizing and Financing
A growing trend in states like Michigan and Minnesota is the development of state government task forces and advisory councils focused on asset management. These groups incentivize owners to have asset management plans in place to improve resiliency and sustainability. By having a management plan, asset owners and communities can properly identify at-risk areas that require updating and meet evolving state and federal climate goals. With a plan in place, communities can take advantage of the substantial federal investments for sustainable infrastructure from programs like the Infrastructure and Jobs Act (IIJA) or state infrastructure grants and legislation.
For example, the IIJA has provided upwards of $7.5 billion for the purpose of updating outdated infrastructure to improve climate friendliness and the ability to withstand climate-related disasters. Without a quality asset management team and plan in place, communities could easily miss out on these opportunities.
How WSB Can Help
WSB’s multidisciplinary team includes experts in asset management who understand sustainability practices and policies, as well as how infrastructure is impacted by natural environments and climate-related issues. By staying at the forefront of techniques and technologies like the use of 3D modeling and automated data collection systems, asset stakeholders, elected officials and the public will have all the information necessary to make the most informed decisions. We work with communities to create a holistic, comprehensive asset management approach that brings real value and is customized for your community or project.
Shannon has spent over a decade advancing asset management at local, state, and national levels by serving on asset management committees, advisory panels, and project management teams. While working at MnDOT, Shannon directed the agency-wide asset management planning including projects, research, policy, innovation, strategic planning, and implementation in collaboration with internal and external stakeholders.
[email protected] | 651.492.9291

Jack is an Asset Management Specialist with degrees in both Geography and GIS and worked as a GIS Technician for an oil & gas consultant for two and a half years. After transitioning into survey, he came to WSB where he works on projects for civil engineering, land development, and planning by collecting field data and completing documentation via use of survey equipment and land record maps. His background in GIS and infrastructure allows him to bring a unique perspective to asset management.
[email protected] | 612.518.4263