By Tony Havranek, Sr. Ecologist, WSB
Implementing the Modified Unified Technique on Hanson Lake.
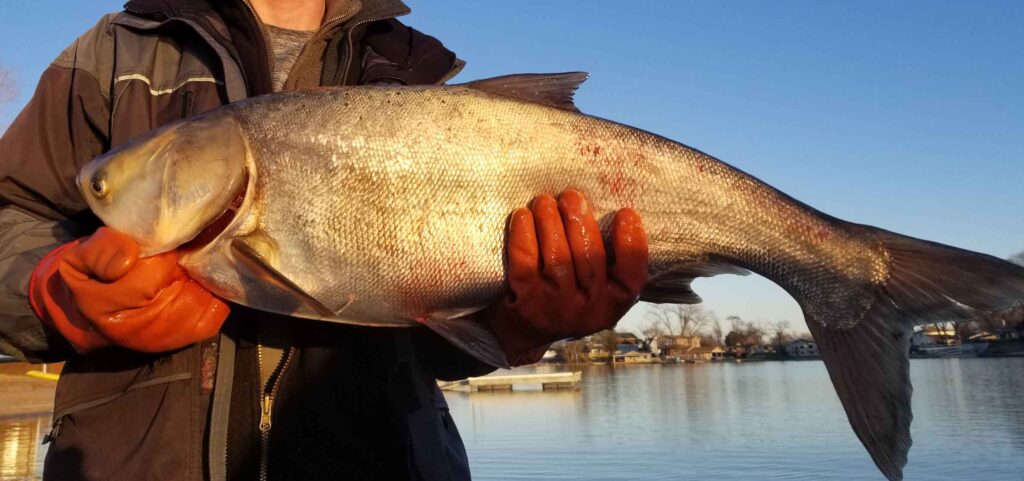

Asian carp are some of the newest invaders of our lakes, rivers and streams. Asian carp is a term used collectively to describe bighead carp, black carp, grass carp and silver carp. Fast growing and invasive, these specific fish are causing problems along the Mississippi River and surrounding bodies of water.
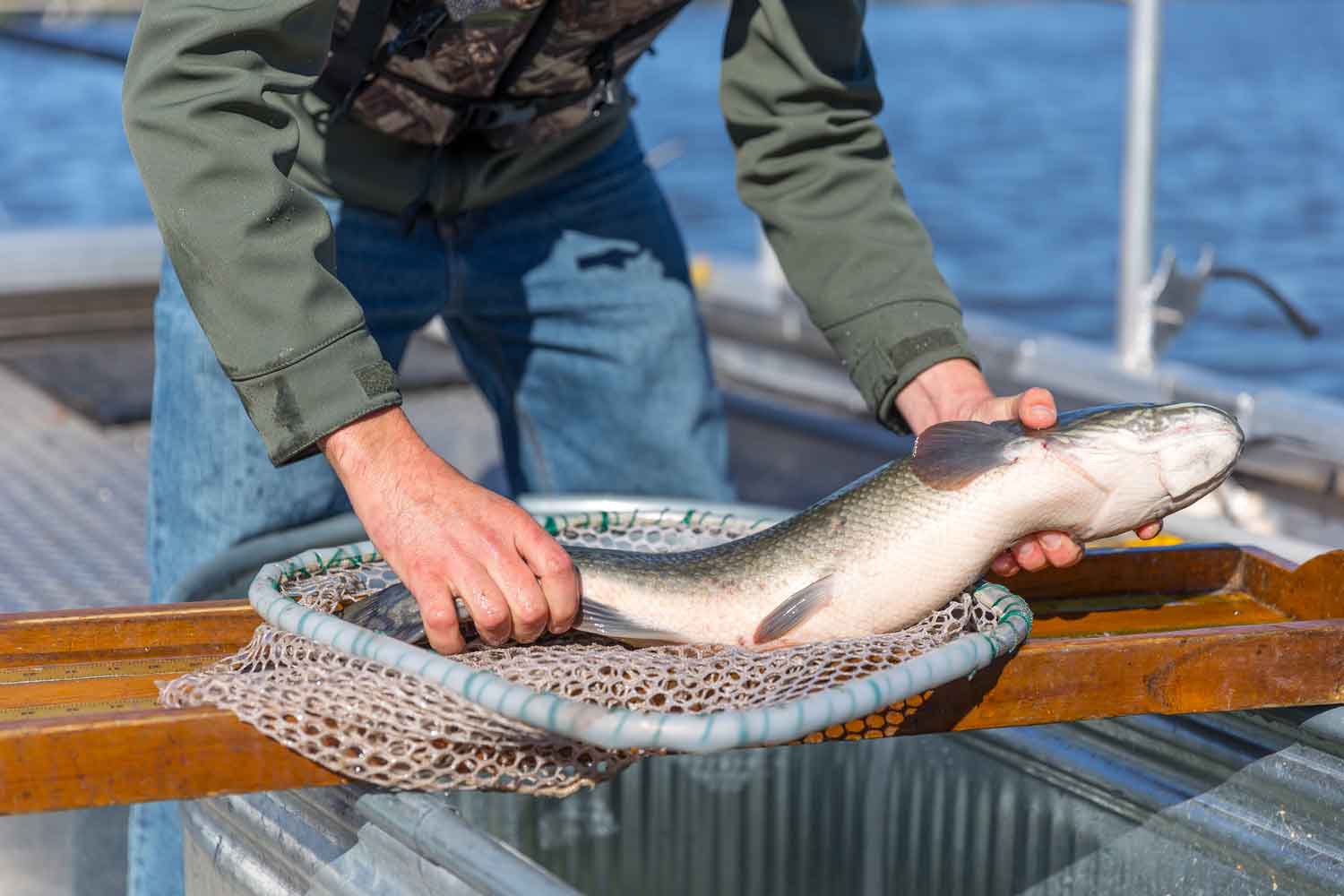
Asian carp are labeled as invasive because of their effect on ecosystems, water quality and native fish populations. Like the Common carp, Asian carp are highly invasive and have disrupted our food web. In 2019, Hanson Lake #3 Homeowners Association (HOA), located in Nebraska, commissioned the WSB natural resources team to address the growing Asian carp population in the lake. The lake’s recreation had taken a hit because of the carp’s ability to fly out of the water, disrupting boaters and swimmers.
Hanson Lake is unique. In the past, commercial fishing crews had identified high populations of Asian carp, but effectively trapping and netting the fish was challenging due to obstructions at the bottom of the lake. These obstructions were preventing the nets from capturing the fish.
With many non-nettable locations located throughout Hanson Lake, we needed to find a solution that would drive the invasive carp into areas where we could capture and extract them. A few years ago, I read about a new harvesting technique developed in China called the modified unified technique. Using this technique, fish are herded into a concentrated area where they can be easily netted and harvested. The technique requires the use of underwater speakers and block nets.
In collaboration with the United States Geological Survey (USGS), we decided to implement the Modified Unified Technique on Hanson Lake. We connected underwater speakers to amplifiers and played a pattern of noises including ice cracking, feedback, human voices, gunshots and hammering. The pattern of noises was played on repeat to begin herding the fish into the waiting nets. Throughout several days, the sound waves drove the fish into the nettable areas of the lake where seine nets were placed.
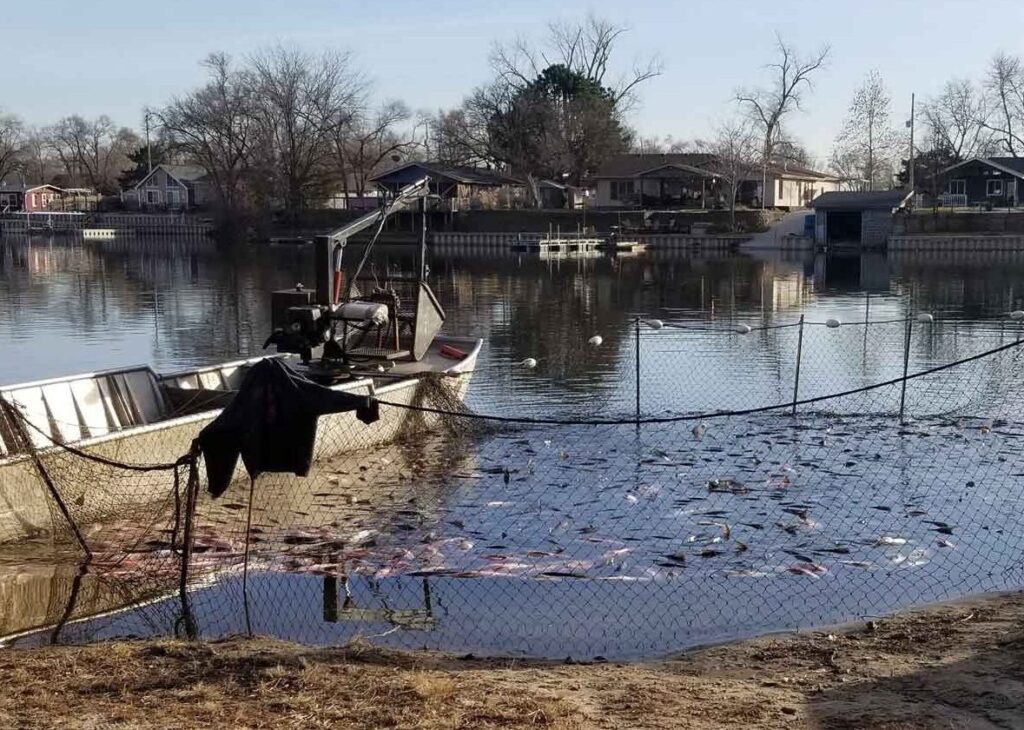

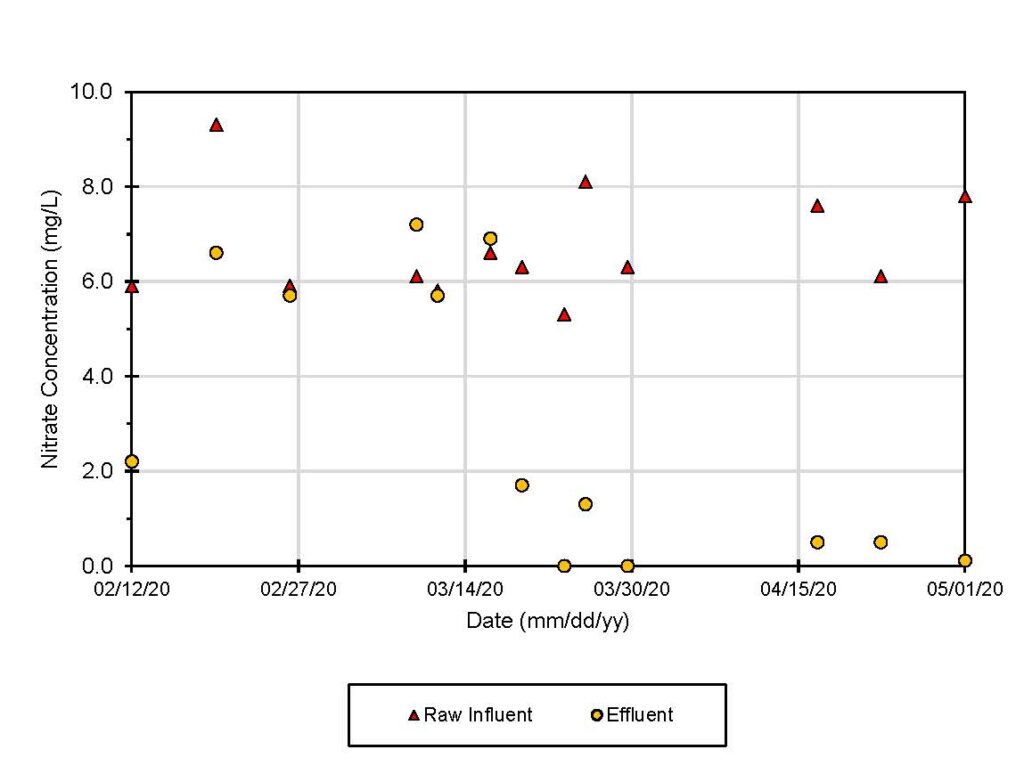
Once the harvest was complete, over 26,000 pounds of rough fish were removed from Hanson Lake. Comparatively in 2018, 8,200 pounds of fish were removed from the lake. Rough estimates indicate that over 30 percent of the lake’s rough fish were removed during this operation which will significantly improve recreation and water quality in the area.
What’s so bad about Asian carp?
Aquatic Invasive Species are behind some of the most drastic changes to freshwater systems in the world today. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Asian carp were first brought to the United States for use in aquaculture ponds. These fish have now invaded the Mississippi River that connects to many bodies of water throughout the nation. Natural Resources organizations and groups are fearful that Asian carp will invade the Great Lakes which would have a severe impact on recreational and commercial fisheries. Many cities, counties and watersheds are taking proactive steps to mitigate the invasive species to protect and preserve the ecology and water quality throughout the nation.