September 18, 2023
By Behnaz Beladi, Director of Renewable Energy, WSB
WSB knows the importance of creating resilient and sustainable cities that prioritize the needs of its residents while preserving the environment. Smart cities that utilize technology to collect data and improve operations are crucial in advancing toward a more sustainable future. Renewable energy has emerged as a critical strategy in achieving this goal and is being implemented and managed in various ways across smart cities.
Here are several key benefits and challenges of implementing renewable energy in smart cities:
Reducing Emissions
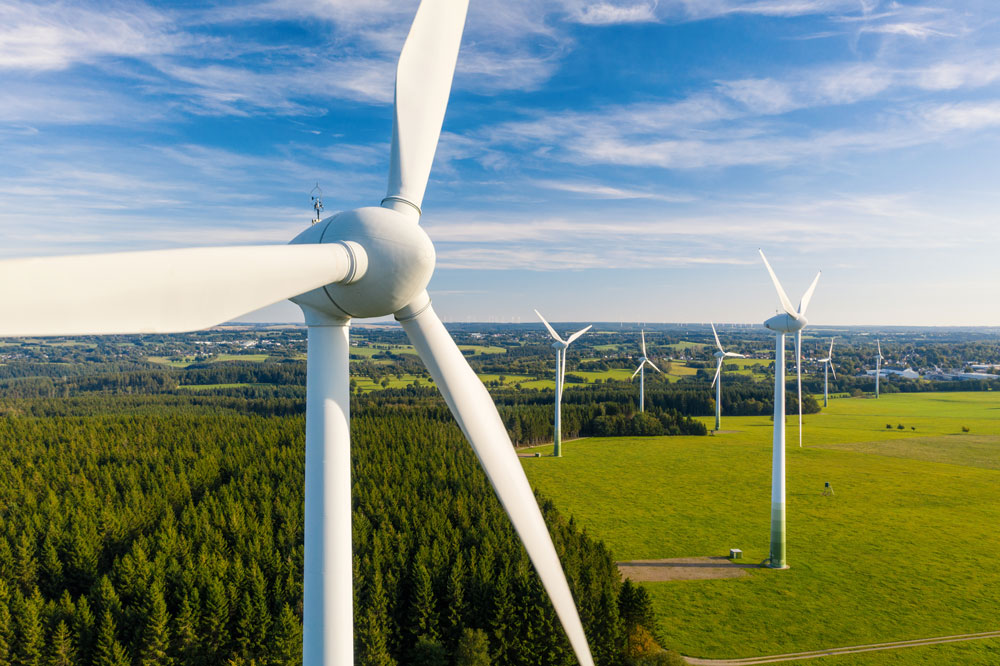
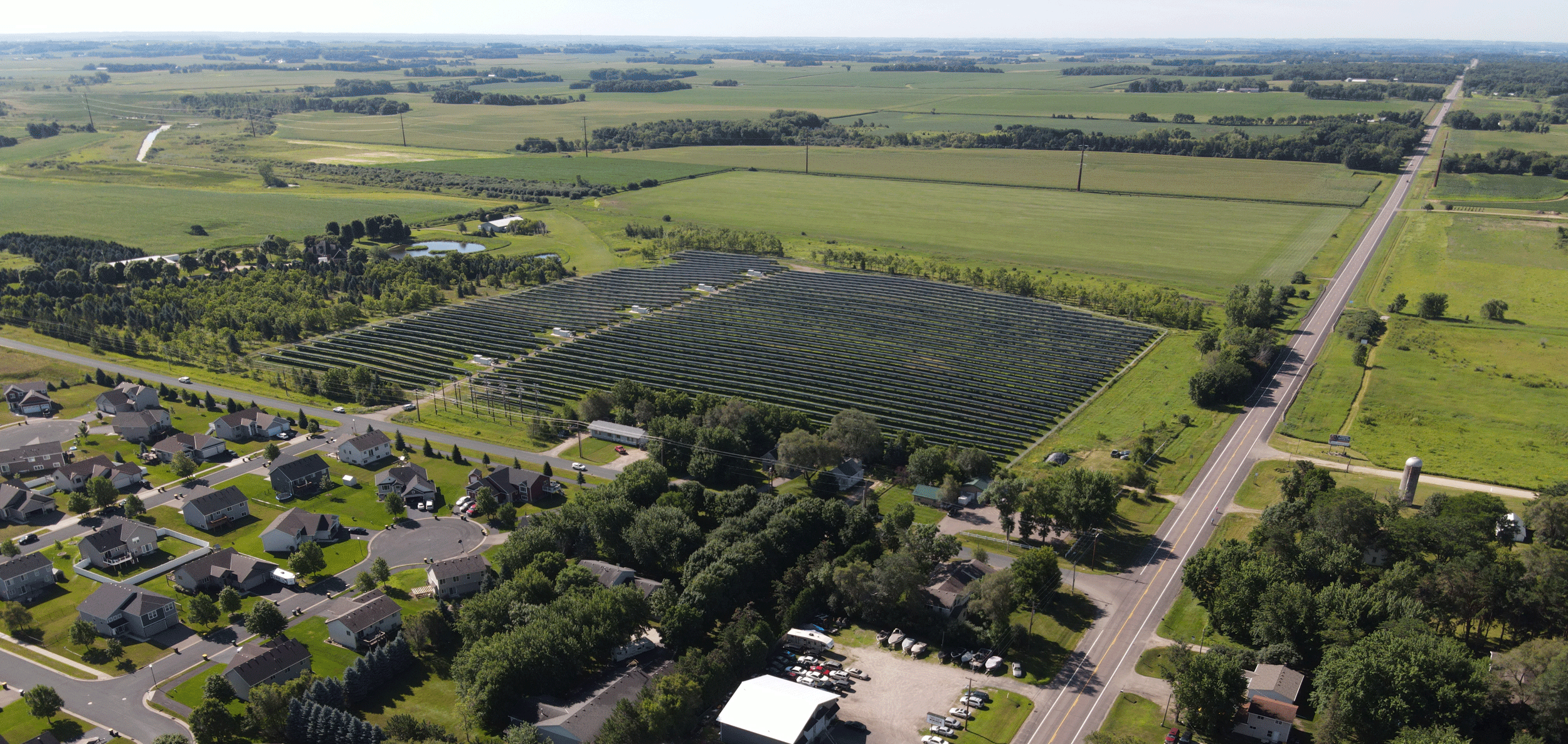
An important benefit of using renewable energy in smart cities is that it helps reduce carbon emissions. By using distributed energy resources such as wind and solar power, smart cities work towards reducing their carbon footprint to zero. This helps the environment and makes the city a desirable place to live and work.
Economic Growth
One of the most significant benefits of renewable energy in smart cities is the potential for economic growth. Affordable and reliable renewable power can attract and retain companies, provide green jobs, and encourage entrepreneurship and innovation through renewable business incubators.
Quality of Life
Public health and safety can be improved through emission free cities. Renewable energy increases the quality of life for residents, particularly those in lower-income households. Inclusivity is promoted by providing access to renewable resources and grants to help cover the costs for low-income residents. Furthermore, residents can be paid to redistribute excess energy back into the grid, providing additional financial support to those needing it.
Challenges
Despite these benefits, there are still challenges to implementing renewable energy in smart cities. To sufficiently leverage renewable sources, a great deal of new transmission infrastructure is required. Power transmission infrastructure was built with large fossil fuel plants and nuclear plants in mind. This raises issues for renewable energy sources not located near existing infrastructure. In fact, some areas with little or no infrastructure, such as off-shore wind farms, are some of the best hopes for sources of renewable energy. In some cities, it may be more difficult to build power plants due to geography, regulations and policies, or issues with constructability. However, through technology and innovation, WSB helps cities find ways to utilize existing infrastructure while being incredibly cost-effective in the long run. This includes incorporating smart EV chargers into commercial buildings and condominiums, helping with solar needs for residential or commercial buildings, and designing wind and solar power plants for cities and utilities.
How WSB Can Help
Renewable energy is an essential component of any smart city. By reducing carbon emissions, driving economic growth, and improving the quality of life for residents, renewable energy is helping to create cities of the future. As more communities adopt renewable energy practices, WSB is here to help design and build new infrastructure or incorporate renewable energy sources into existing infrastructure.
Behnaz manages the multi-disciplinary renewable energy team in project and program operations. She is an accomplished academic, with a PhD of Mechanical Engineering from the Technical University of Vienna, an associate of the North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP) and has served on the board of the Minnesota Solar Energy Industries Association, advocating for policy and regulatory initiative’s that strengthen the industry.
[email protected] | 612.468.8423