December 18, 2023
By Bob Barth, Director of Land Development, WSB
A visionary redevelopment project in St. Paul.
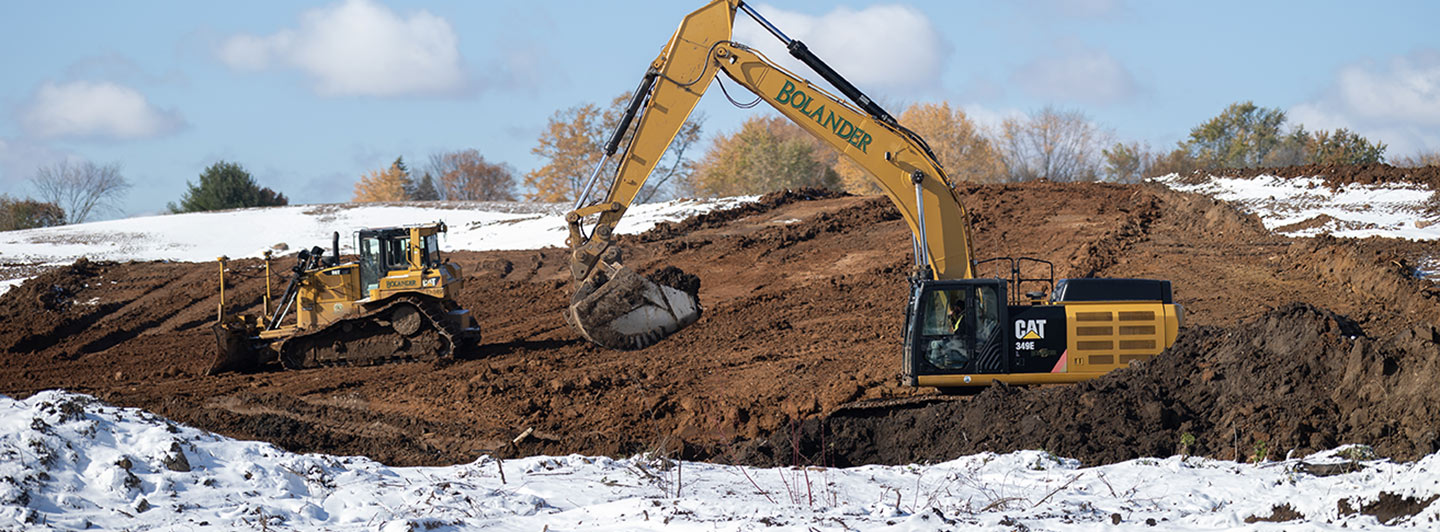
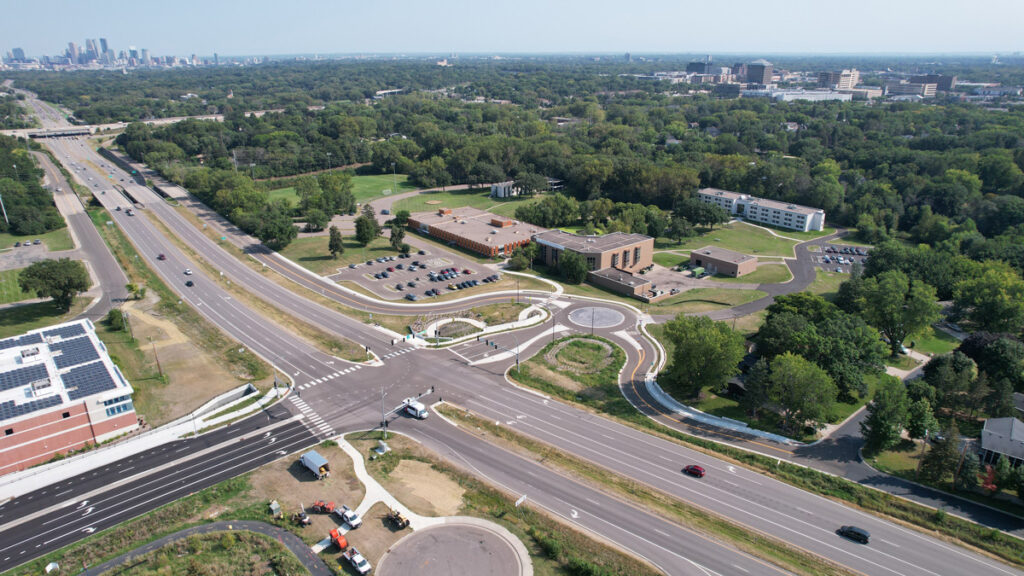
When the Saint Paul Port Authority saw an opportunity to purchase the Hillcrest Golf Course in 2019, they sought WSB’s infrastructure planning and design experience to breathe new life into the 112-acre property on Saint Paul’s east side. Four years later, this unique project is under construction and promises new jobs and housing, expands the local tax base, achieves multiple green outcomes, and interweaves publicly accessible open space into its employment and residential settings.
The Challenges & Opportunities of the Project
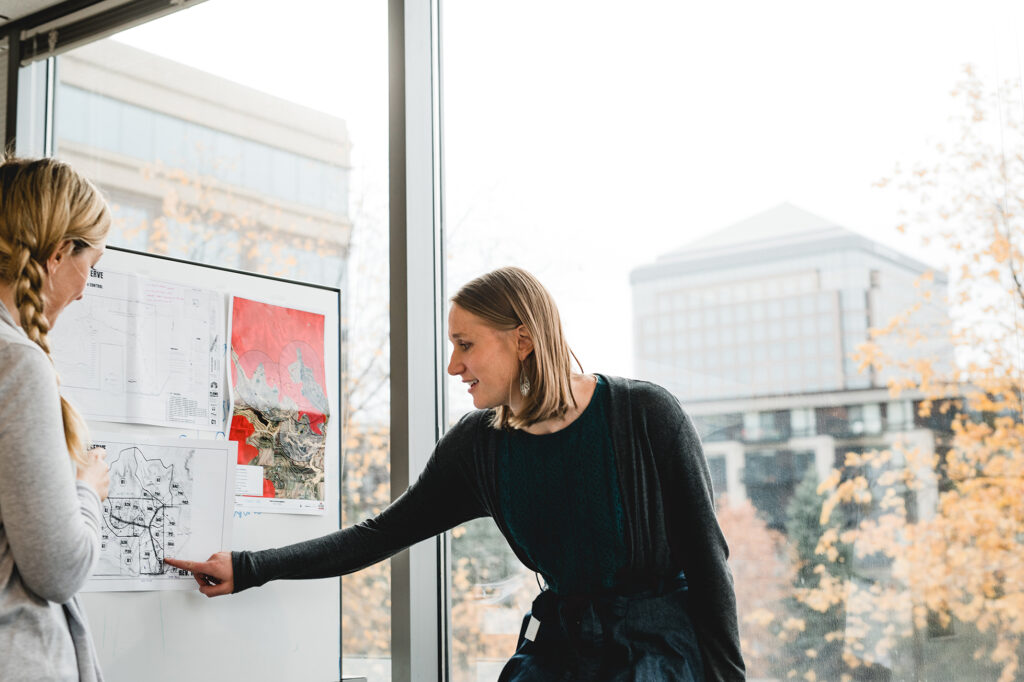
The Hillcrest transformation into the Heights can be mapped across several stages: pre-purchase due diligence, master planning, design and construction. We joined forces with the Saint Paul Authority and other partners for landscape and sustainability to tackle these phases head-on, understanding the complexities of the project, as well as the great value it will bring to the community upon completion.
One problem that had to be mitigated was mercury contamination on the site, due to chemicals used on the property when it was a golf course. Also, the property’s uniquely hilly terrain had to be adapted to industrial development, new roads and infrastructure. Remediation plans to clean up the site and ensure the design accounts for the landscape were critical for this project.
Crafting Community Space
At the heart of this redevelopment lies the aspiration to create a space accessible to the public – one boasting open spaces, park-like areas and captivating public art displays. The idea is that no matter where someone is, people are close to nature.
There will be one million square feet of industrial space and one thousand new housing units, driving economic prosperity and diversity in the area. This a public project, and at its heart, it is focused on the greater needs of the community and how to develop a project that brings critically needed housing, jobs and opportunities for the east side’s residents and its emerging young workforce.
An Accelerated Timeline for Community Need
Originally slated as a decade-long endeavor, the Heights redevelopment project gained momentum due to overwhelming demands and protentional to uplift the area. Substantial completion is expected in 2025, with full project completion in 2026.
A Chance for Change
Our firm’s involvement in this transformative venture was no accident. The choice was driven by a deep-rooted experience in working with project partners like the City of St. Paul and Ramsey County, and a shared commitment to projects that elevate diversity and prosperity. With a profound understanding of the region’s pulse and a dedication to inclusivity, WSB was proud to be a partner to turn the Heights vision into reality.
Forging a Brighter Future, Together
As Hillcrest Golf Course evolves into The Heights, a hub of vibrancy and opportunity, the collaborative efforts of the Saint Paul Port Authority, WSB and other visionary partners amplify the community’s prospects. From navigating complex terrain to envisioning inclusive spaces, this project speaks to a brighter, more sustainable future for the east side of St. Paul – one defined by innovation, diversity, and an unwavering commitment to transformation.



Bob leads WSB’s Land Development Services. Over his 26-year career, he has worked for both public and private sector clients, beginning as a water resource engineer and evolving into his current land development role. Bob’s current interest and a focus for WSB’s Land Development Group is sustainable redevelopment within urban communities.
[email protected] | 763.231.4876