January 11, 2023
The Foundation of Digital Delivery
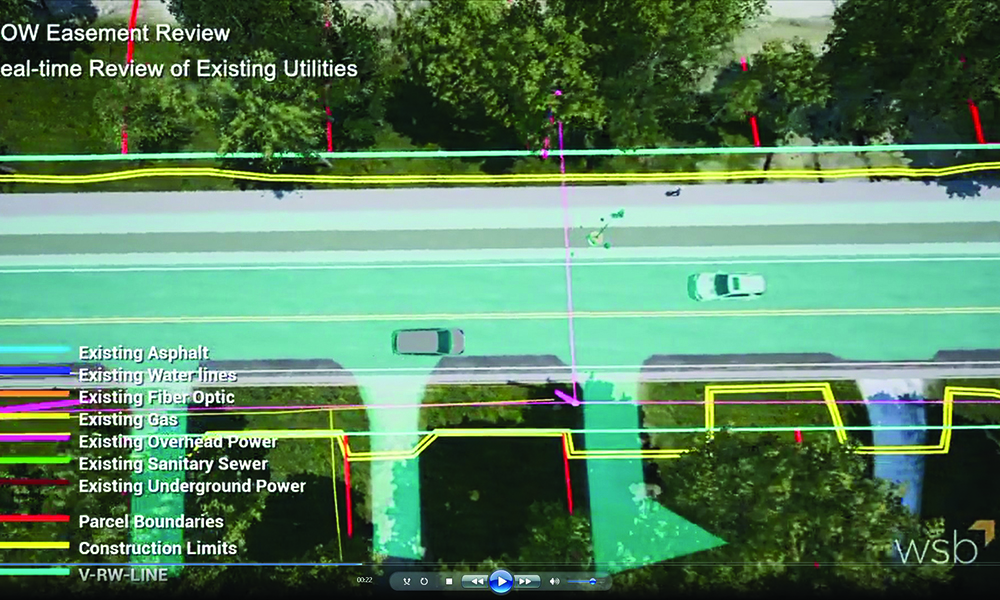
Geospatial data is information that involves large sets of data gathered from a variety of diverse sources based on location. In the Architecture, Engineering and Construction (AEC) Industry, we depend on geospatial data to build and design infrastructure. Strong data is the foundation of any digital delivery project. Capturing geospatial data for infrastructure projects is the first step in the digital delivery workflow.
The five ways we gather thousands of accurate data points to improve design methods and increase speed and accuracy.
Reality Capture for 4D / 5D
High resolution drones capture thousands of photos that overlap at different angles to create a geospatially accurate reality capture of an entire site. The reality capture contains accurate lengths, depths, and heights. To increase accuracy, the geospatial data is tied to survey ground control points. Once the data is processed, it can be input into many different design software, serving as the first step in digital delivery.
Interior/Indoor Scanning
Using a tripod and LIDAR scanner, we collect thousands of data points. The scanner is moved around to cover the entire area, capturing points along the way, and is then uploaded into BIM software. This information can be used to create a robust asset management system.
WSB 360 – Google Street View
WSB 360º captures high-resolution 360º imagery that is used to detect and map a variety of assets as they exist today. Google imagery is often missing or out-of-date. By driving a street or an alley, data is gathered within minutes and uploaded to Google Maps and StreetView. This technology is also used to capture, map, and classify road assets including hydrants, signs, power poles, and streetlights.
Traditional Surveying
Traditional surveying is performed by survey crews using tools to make measurements. Some refer to this as the most accurate form of data collection because of the boots on the ground element. There are proven methods of verifying accuracy and conventional survey has been performed for hundreds of years.
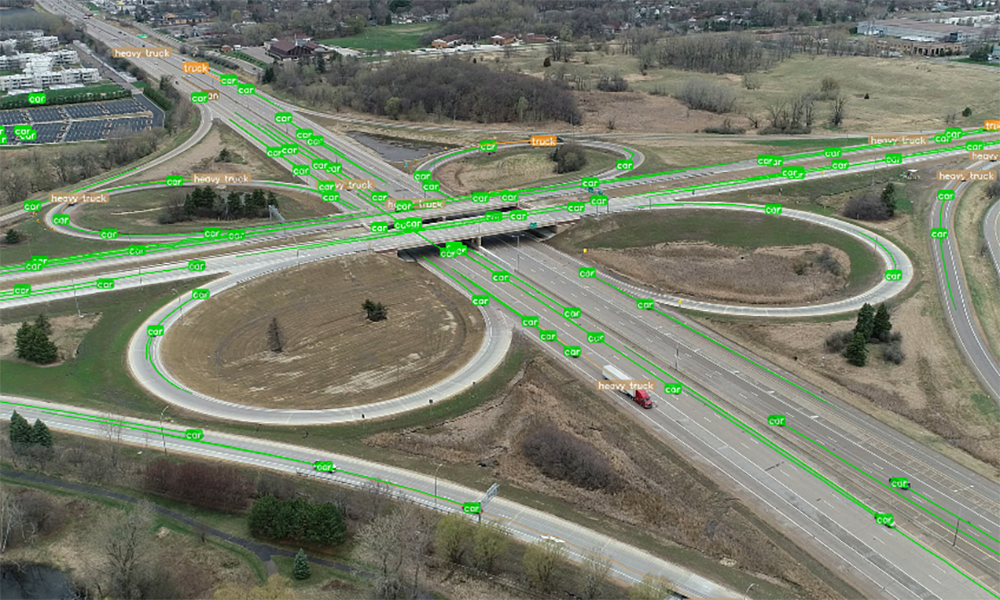
Conventional Drone | 2D & 3D Reality Captures
With conventional drone data, we create 2D and 3D high-resolution imagery. This data serves as the foundation for 3D and 2D reality captures. 3D reality captures are developed when elevations are needed for digital design. 2D reality captures are developed when elevation isn’t necessary. In the past, satellite imagery was relied upon, which was often inaccurate and outdated. Through conventional drones, we can document a site accurately, in-depth, and within minutes.
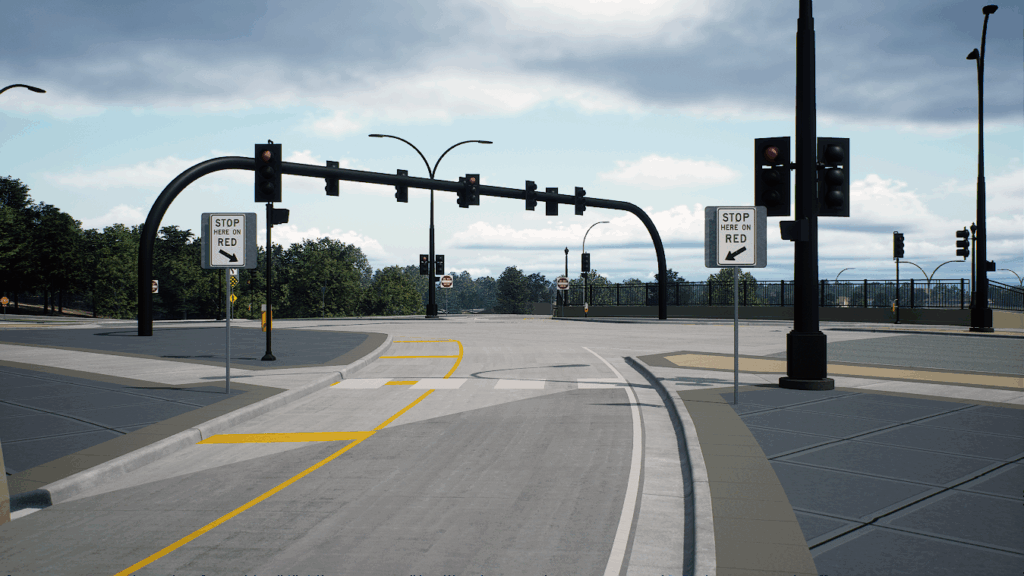
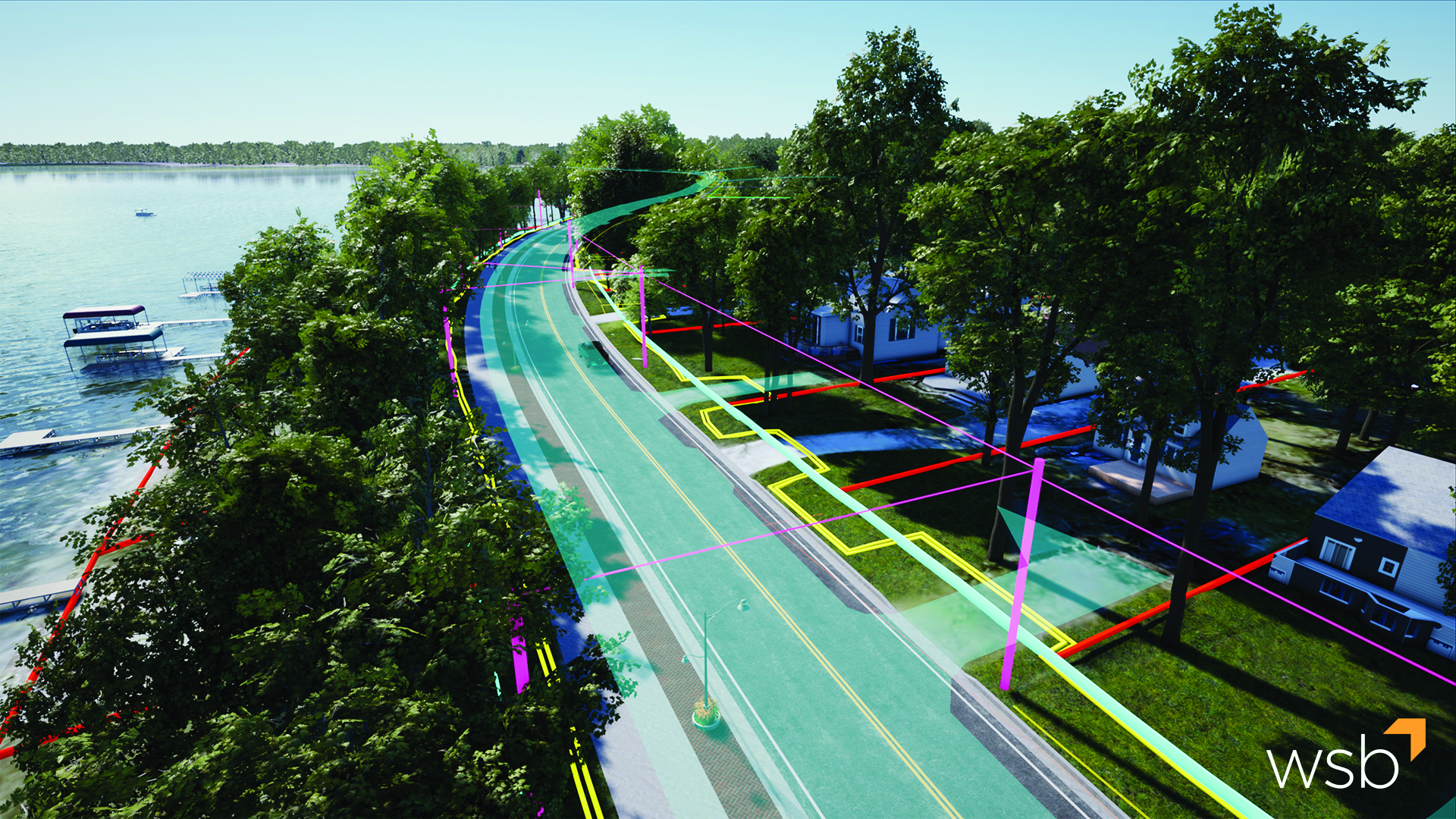
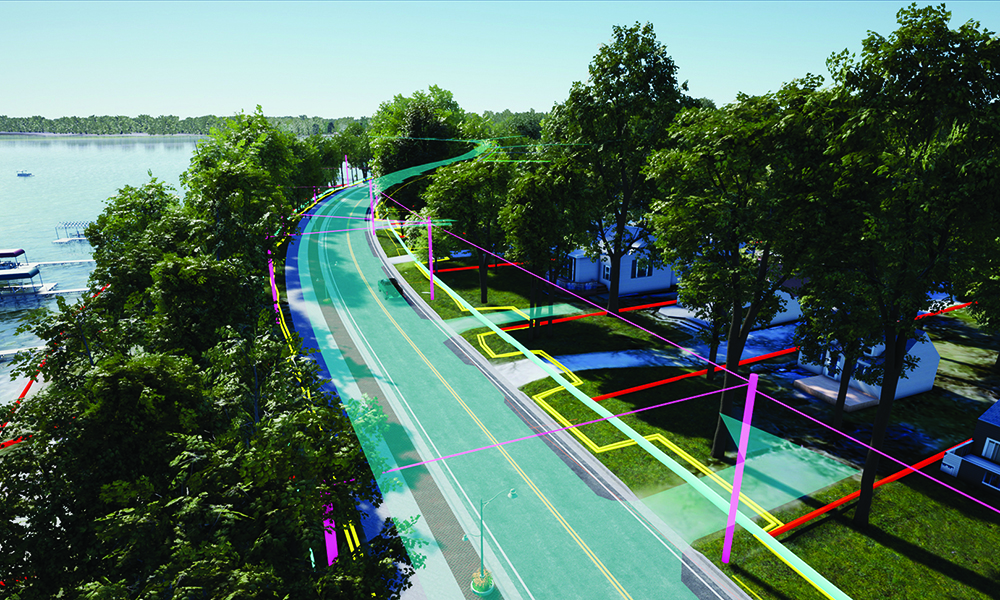
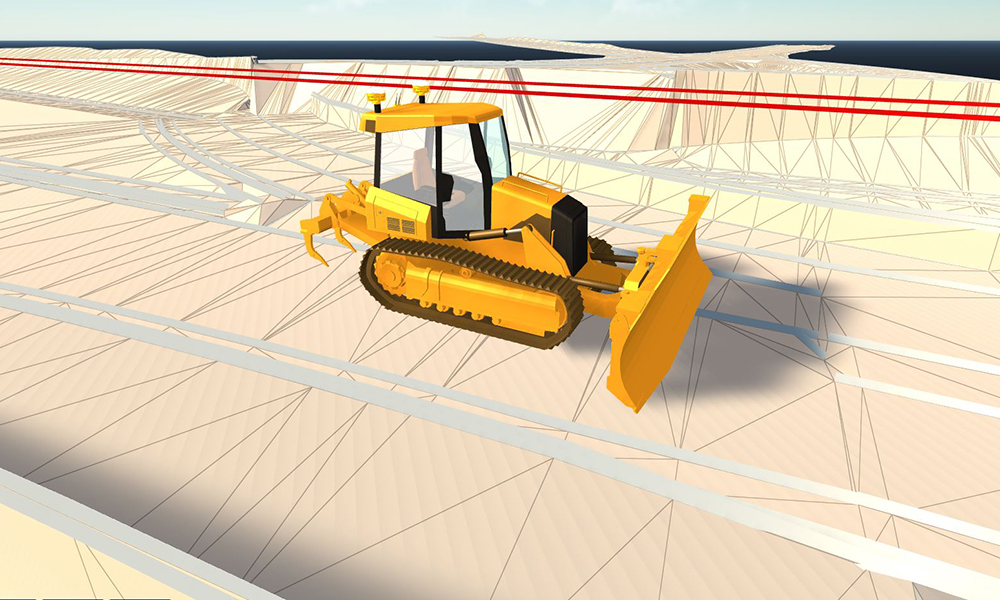
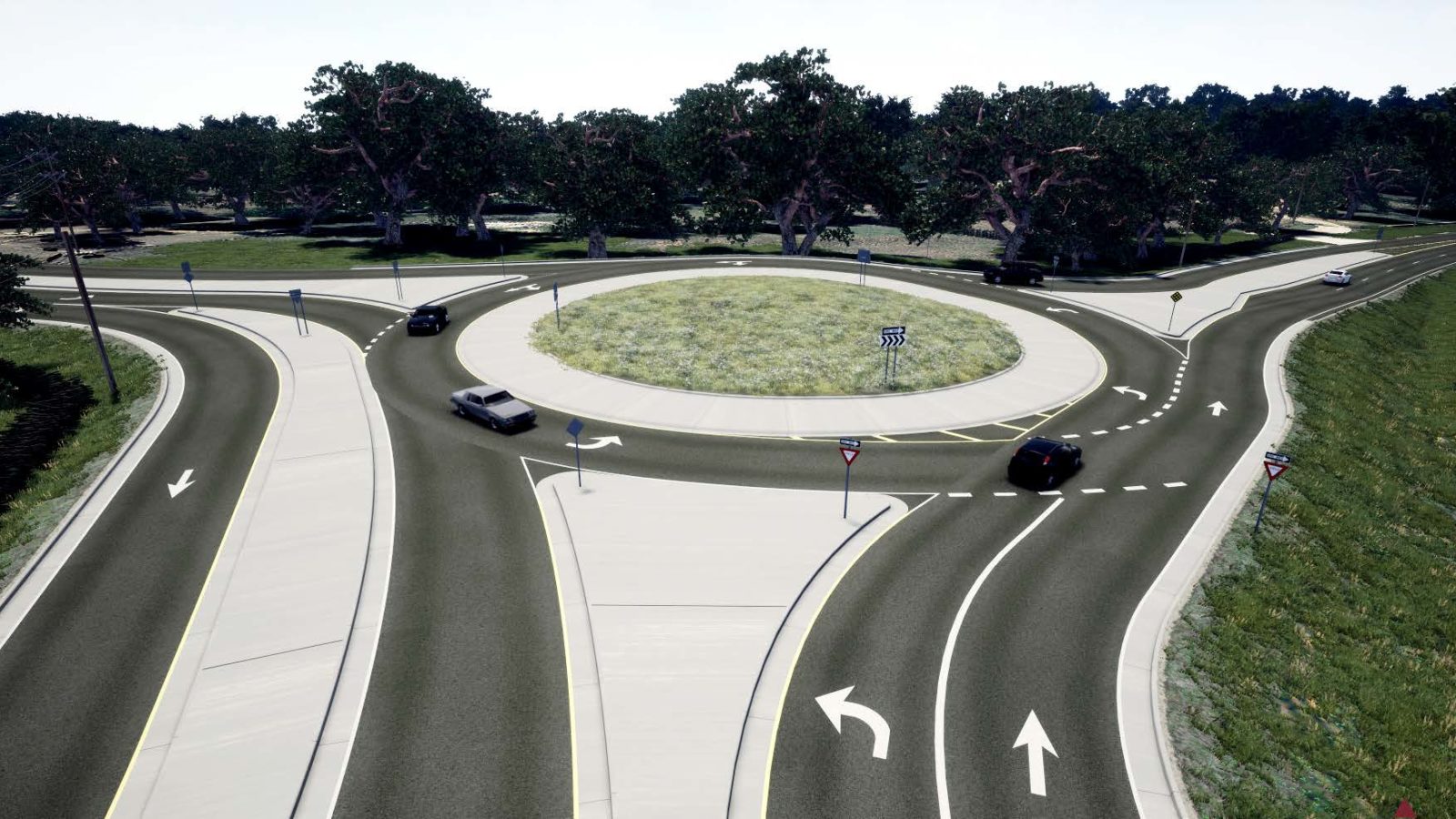







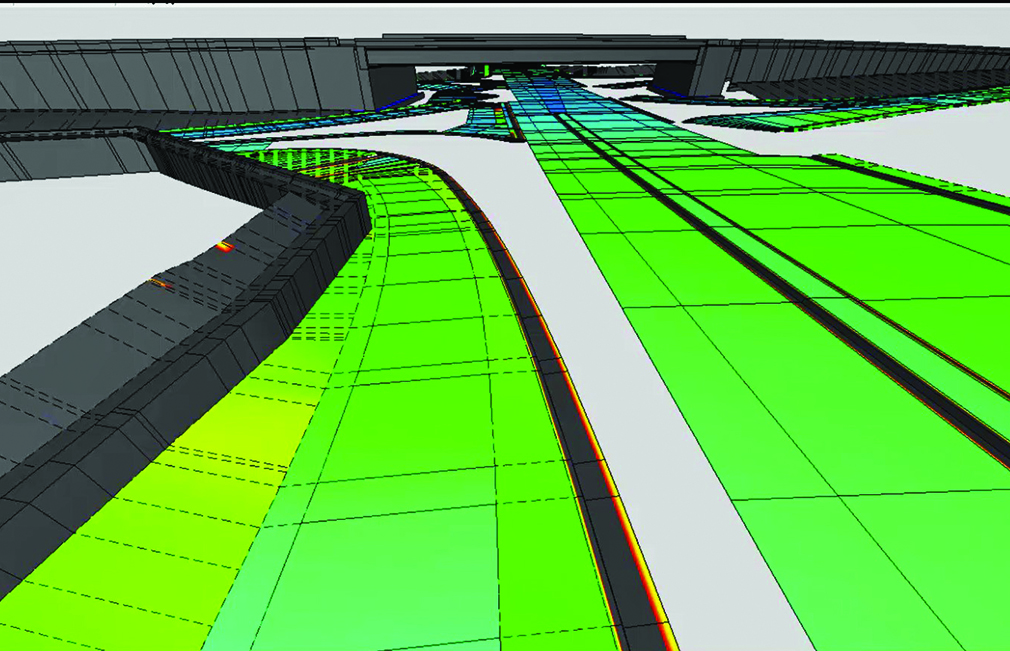
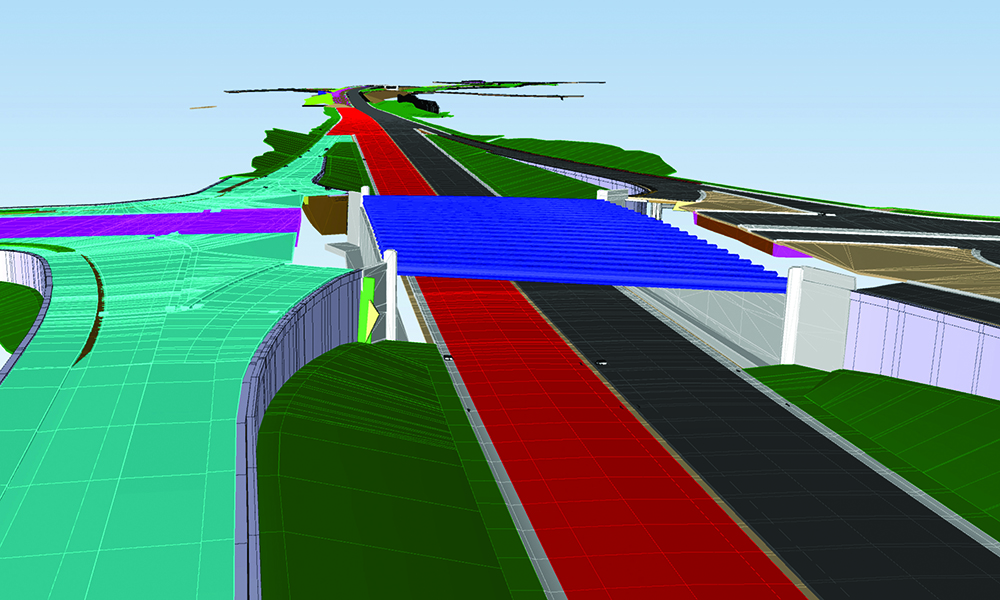
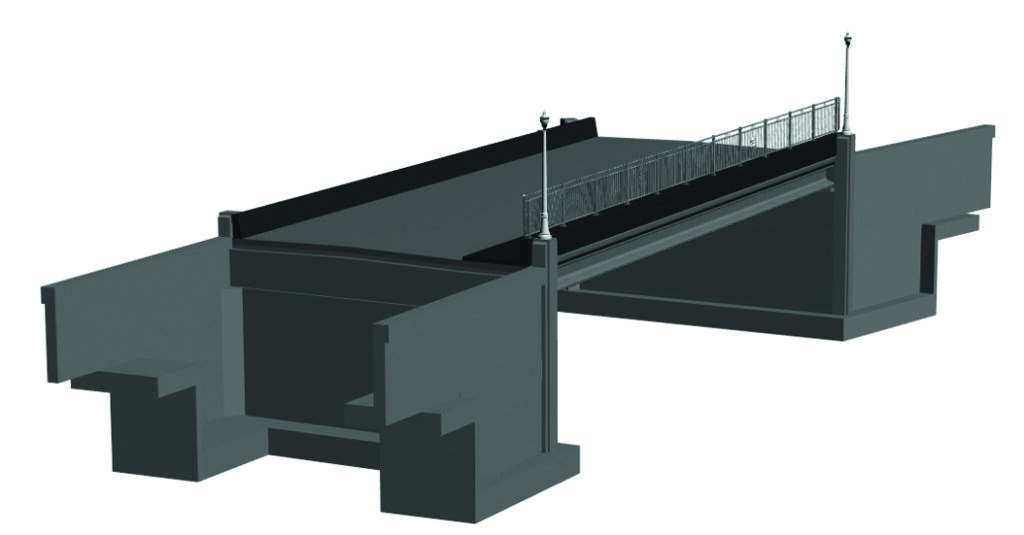
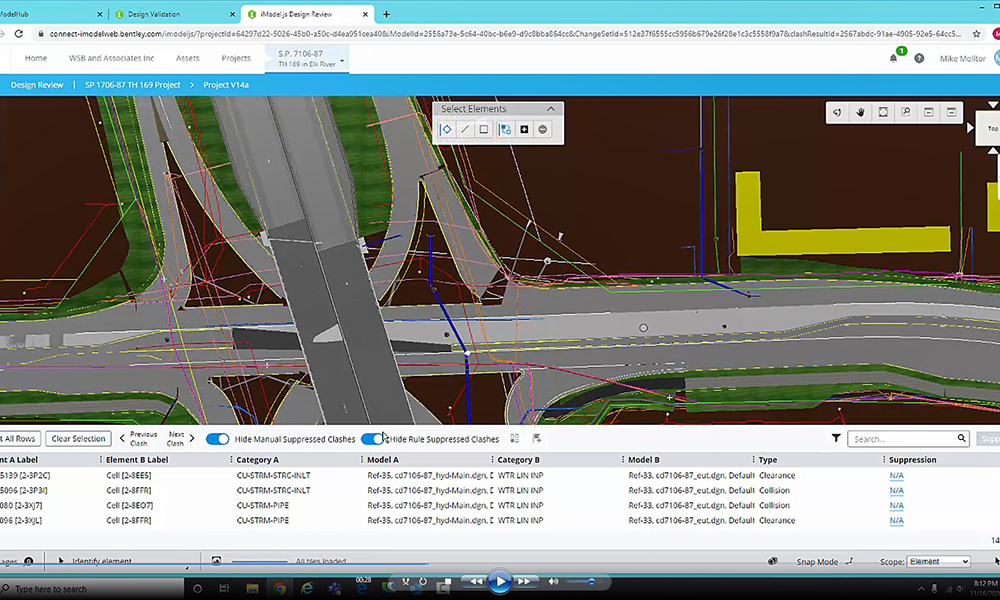




 Up until last month, real-time and ray tracing couldn’t be used in the same sentence without a bank of 10 GPUs and 2500 watts of power. Ray tracing makes renderings dynamic and realistic and thanks to powerful GPUs, shortens the amount of time spent on each frame. This recent advance in technology allows clients and the public to see reflections, higher quality shadows and experience the creation for themselves. Today, we’re utilizing these technologies to create stunning visualizations for our clients. Once the projects have been modeled, iterations are produced in minutes, instead of days or weeks.
Up until last month, real-time and ray tracing couldn’t be used in the same sentence without a bank of 10 GPUs and 2500 watts of power. Ray tracing makes renderings dynamic and realistic and thanks to powerful GPUs, shortens the amount of time spent on each frame. This recent advance in technology allows clients and the public to see reflections, higher quality shadows and experience the creation for themselves. Today, we’re utilizing these technologies to create stunning visualizations for our clients. Once the projects have been modeled, iterations are produced in minutes, instead of days or weeks.